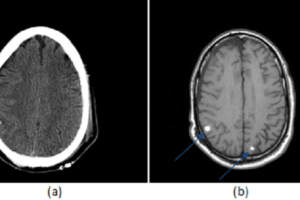
Nerve roots distal to the termination of the spinal cord comprise what is called the cauda equina (CE). Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is low back pain, typically bilateral, saddle sensory disturbances, variable... Read more »
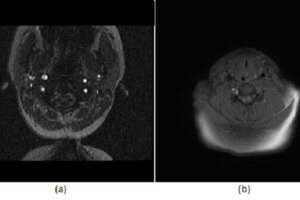
Carotid/vertebral artery dissection is an underdiagnosed disease that can result in substantial morbidity. It has an incidence of 1-1.5/100000 and disproportionately affects young patients. Diagnosis is challenging clinically because the symptoms are... Read more »
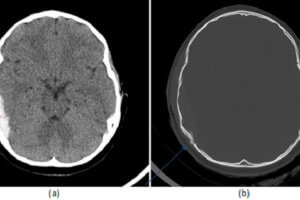
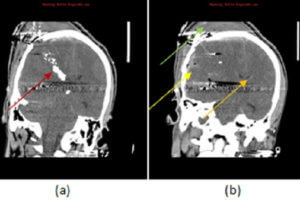
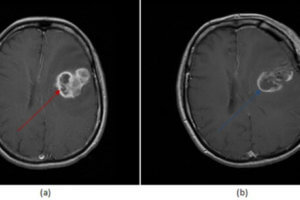
The third T in the 3T trauma framework (see cases on epidural hematoma and penetrating trauma) refers to “other targets” and concerns delayed complications of traumatic brain injury. These competitions include hydrocephalus,... Read more »
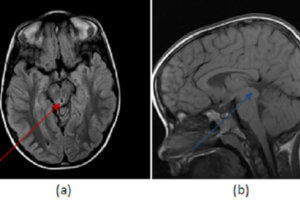
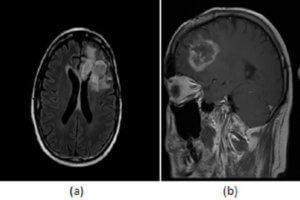
Masses of the pineal region can be divided into pineal and non pineal. Non pineal masses can arise from any of the structures in the region and include glioma (from the tectum... Read more »
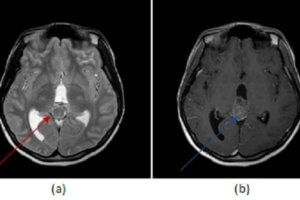
Tumors of the pineal gland can be categorized into pineal cell and germ cell depending of their cell type of origin. Unlike germ cell tumors, pineal cell tumors tend to expand the... Read more »