Cefepime is a cephalosporin antibiotic typically used when broad spectrum coverage including Pseudomonas aerigonsa is needed. However, it can produce cefepime neurotoxicity with encephalopathy, myoclonus, reversible aphasia, and/or convulsive or subclinical seizures. Read more »
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) is one of the most common generalized epilepsy syndromes and typically presents in the teen years. Like absence epilepsy, it is considered a primary generalized epilepsy, rather than... Read more »
Absence epilepsy is a type of primary generalized epilepsy in children, and usually presents as staring spells. Read more »
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II (CPT) deficiency is the most common inherited lipid-metabolism disorder in skeletal muscle. Read more »
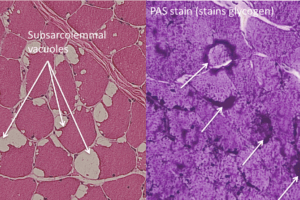
McArdle disease is a glycogen storage disease in which the enzyme muscle myophosphorylase is deficient. It is commonly known as glycogen storage disease V. Read more »
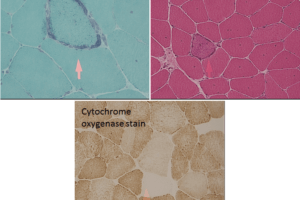
Mitochondrial myopathy can be caused by metabolic abnormalities related to mutations in the mitochondrial genome or mutations in the somatic genome that produce abnormal mitochondrial proteins. Read more »
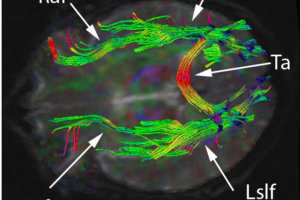
Conductive aphasia is defined as the inability to repeat a spoken phrase, even when comprehension is intact and speech production is otherwise normal. Read more »
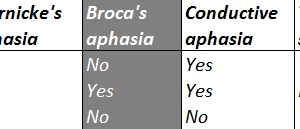
Patients with expressive aphasia have difficultly speaking fluently, although they can understand what other people say when they are spoken to. Read more »
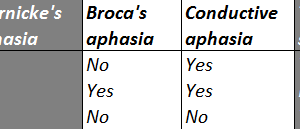
Patients with receptive aphasia can speak clearly (fluently) but cannot understand what others say and have difficulty putting together meaningful sentences. Read more »
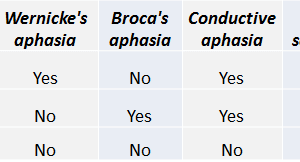
Aphasia is defined as a loss of the ability to understand or produce speech, usually caused by damage to the cerebrum. It is important to clinically classify the type of aphasia a... Read more »
