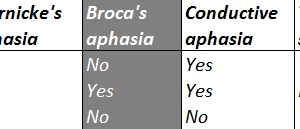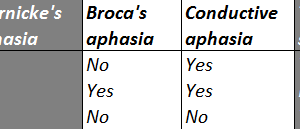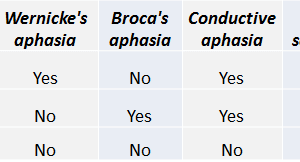
Conductive aphasia is defined as the inability to repeat a spoken phrase, even when comprehension is intact and speech production is otherwise normal.
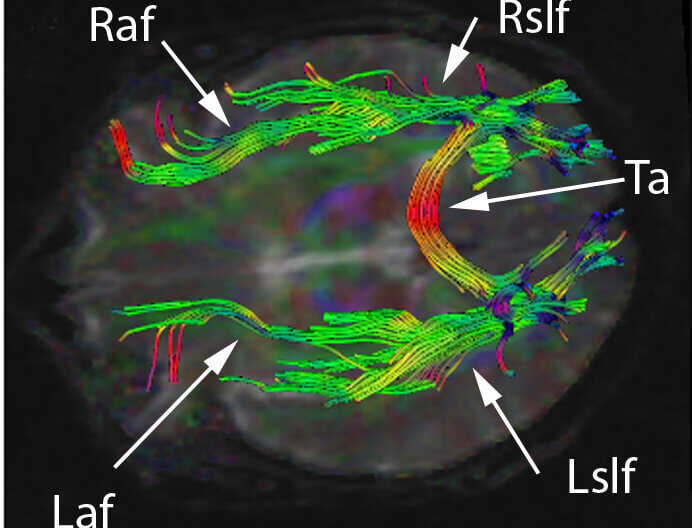
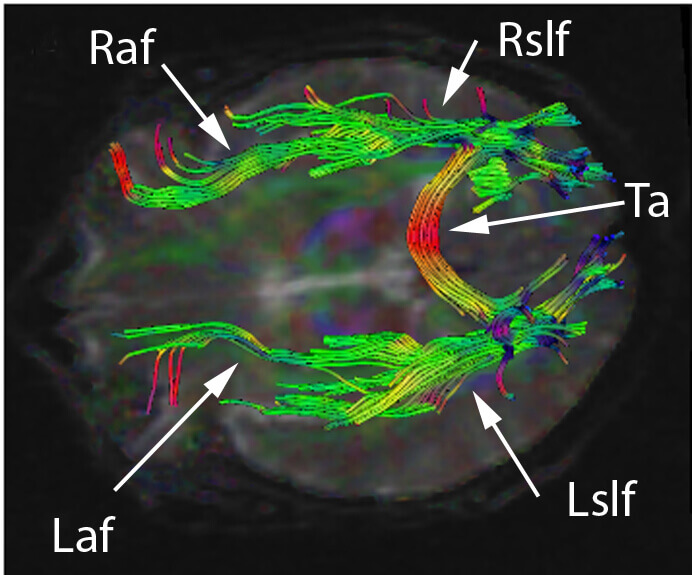
Conductive aphasia is classically caused by lesions to the arcuate fasciculus (usually on the left). The arcuate fasciculus is a curved bundle of axons that projects from Wernicke’s area to Broca’s area. For repetition to be preserved all three areas need to be intact: Wernicke’s, Broca’s and the arcuate fasciculus.
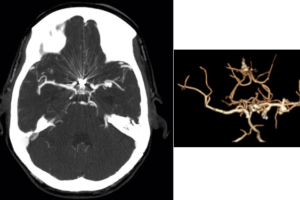
The development of diffusion tensor imaging allows visualization of think white matter tracts, like the arcuate fasciculus. In the image below, the left arcuate fasciculus is labeled Laf
This syndrome should be contrasted to receptive aphasia and expressive aphasia.