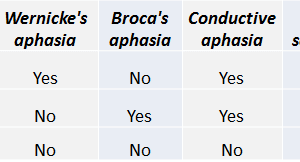
Conductive aphasia is defined as the inability to repeat a spoken phrase, even when comprehension is intact and speech production is otherwise normal. Read more »
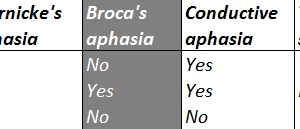
Patients with expressive aphasia have difficultly speaking fluently, although they can understand what other people say when they are spoken to. Read more »
Patients with receptive aphasia can speak clearly (fluently) but cannot understand what others say and have difficulty putting together meaningful sentences. Read more »
Aphasia is defined as a loss of the ability to understand or produce speech, usually caused by damage to the cerebrum. It is important to clinically classify the type of aphasia a... Read more »
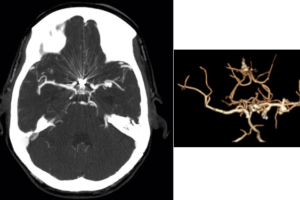
History : 45 year old man with sudden onset of severe headache. What is the most likely etiology for this patient’s intraventricular hemorrhage? Read more »
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APLS; Hughes Syndrome) produces a hypercoagulable state that can predispose to ischemic strokes as well as other thrombotic events. Read more »
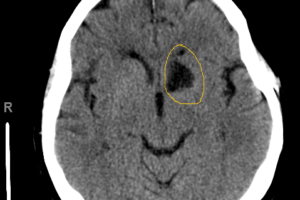
The recurrent artery of Heubner is a branch off the proximal A2 or distal A1 segment of the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and supplies the head of the caudate nucleus, as well... Read more »
A form of trans-cortical motor aphasia (TCMA), Supplementary Motor Area aphasia can occur in strokes of the Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA) on the dominant hemisphere. Read more »
When an area of the brain experiences a sudden loss of blood, the event is called a stroke or cerebrovascular accident. Accompanying this circumstance is a loss of neurologic function. Strokes are... Read more »
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a transient disruption of blood flow to an area of the brain. The event usually last only a few minutes. TIA symptoms occur suddenly and may... Read more »

 Neurovascular disorders including classic large-vessel stroke syndromes, lacunar syndromes, and other vascular abnormalities.
Neurovascular disorders including classic large-vessel stroke syndromes, lacunar syndromes, and other vascular abnormalities.