Carotid/vertebral artery dissection is an underdiagnosed disease that can result in substantial morbidity. It has an incidence of 1-1.5/100000 and disproportionately affects young patients. Diagnosis is challenging clinically because the symptoms are... Read more »
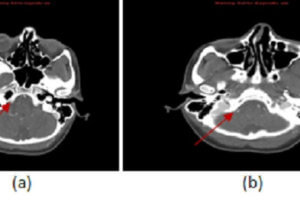
Carotid/vertebral artery dissection is an underdiagnosed disease that can result in substantial morbidity. It has an incidence of 1-1.5/100000 and disproportionately affects young patients. Diagnosis is challenging clinically because the symptoms are... Read more »
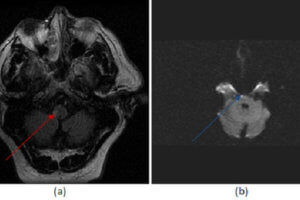
The lateral medullary or Wallenberg syndrome results from an infarct of the lateral medulla from disease in the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) or its branches. The PICA is the first major... Read more »
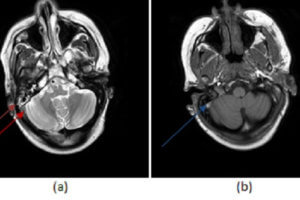
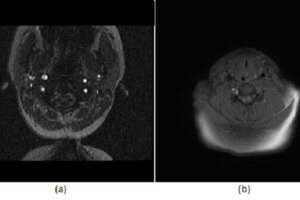
The dural venous sinuses are responsible for draining blood and CSF from the brain. They include the superior and inferior sagittal sinus, straight, transverse, sigmoid and cavernous sinuses. Venous sinus thrombosis can... Read more »
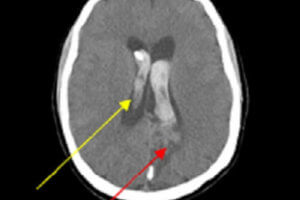
Arteriovenous malformations (AVM’s) are vascular malformations caused by an abnormal communication (arteriovenous shunting) between small arteries and veins without an intervening capillary bed. AVM’s are the most common symptomatic intracranial vascular malformation,... Read more »
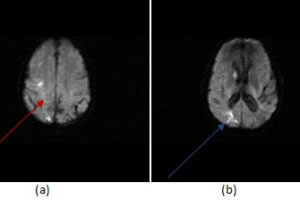
The anterior middle and posterior cerebral arteries supply the majority of the cerebral cortex. However, thin regions of brain at the junction of these vascular territories are relatively under supplied by blood... Read more »
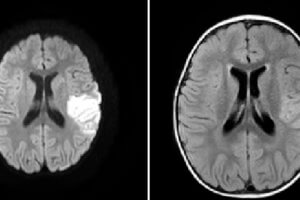
The middle cerebral artery is the major supplier of blood to the cerebral cortex. It consists of 4 principal segments, M1-M4. M1 refers to the horizontal course of the artery from its... Read more »
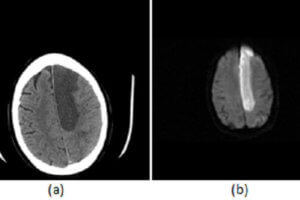
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) consists of 3 major segments, designated A1-A5 . The A1 segment extends from the middle cerebral artery to the anterior communicating artery (a small artery connecting the... Read more »
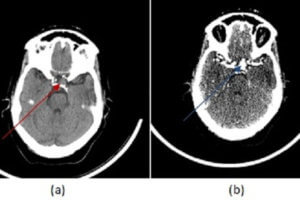
Intracranial aneurysms are dilations of the vascular wall. They can be subdivided according to morphology. Fusiform aneurysms are ovoid and elongated, while saccular ones are circumscribed, and spherical. Fusiform aneurysms are less... Read more »
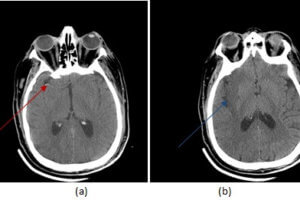
The recent use of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) to treat acute stoke has resulted in the introduction of “code strokes” in many emergency rooms, which typically require the coordinated efforts of... Read more »

 Neurovascular disorders including classic large-vessel stroke syndromes, lacunar syndromes, and other vascular abnormalities.
Neurovascular disorders including classic large-vessel stroke syndromes, lacunar syndromes, and other vascular abnormalities.