Answer: D. Acute Infarct. This is an acute embolic non-hemorrhagic right middle cerebral artery infarct visible on CT. There is a hyperdense right middle cerebral artery with subtle loss of grey white differentiation... Read more »
Whether found as a result of carotid auscultation or as part of a stroke/TIA work up on the contralateral side, there are specific protocols for the treatment of asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Read more »
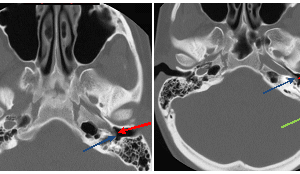
Aberrant course of the internal carotid artery (a-ICA) is a congenital anomaly characterized by the displacement of the ICA posterior and lateral to its expected course. It results from the agenesis of... Read more »
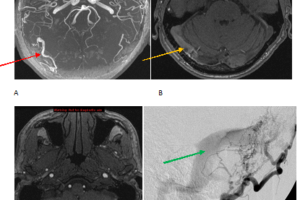
Dural arterio-venous fistulas are a rare but important category of intracranial vascular abnormalities. They are characterized by arterio-venous shunting within the dura and are most commonly a sequelae of trauma. The hypothesized... Read more »
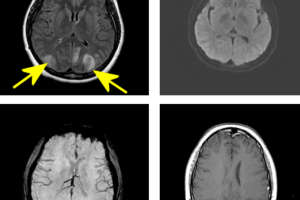
PRES is an disorder of cerebrovascular autoregulation commonly associated with hypertension and previosly referred to as eclampsia. Poor sympathetic regulation of the posterior cerebral arteries makes PRES more likely to involve the... Read more »

Acute infarcts lead to cell swelling in a process called cytotoxic edema. Signal in diffusion weighted MRI (DWI) is inversely related to the degree of brownian motion of intraparenchymal water. When an... Read more »
tPA for ischemic stroke was first approved in 1996 based on the result of two NINDS studies that compared outcomes of placebo or IV tPA given in the first 3 hours of... Read more »
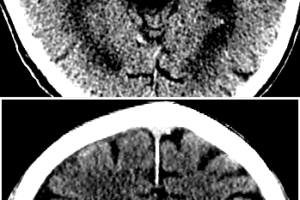
Despite its poor sensitivity for detecting embolic strokes, head CT scan remains the initial imaging modality in the work up of suspected acute stroke. The rationale is to initially rule out hemorrhagic... Read more »

 Neurovascular disorders including classic large-vessel stroke syndromes, lacunar syndromes, and other vascular abnormalities.
Neurovascular disorders including classic large-vessel stroke syndromes, lacunar syndromes, and other vascular abnormalities.