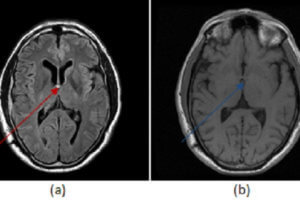
The most common cause for enlargement of the ventricles is ex vacuo dilation due to atrophy of the cerebral parenchyma. It is important to distinguish ex vacuo ventricular dilation from true enlargement... Read more »
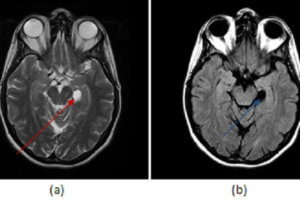
Hydrocephalus refers to enlargement of the ventricular system and two broad categories are recognized – communicating and noncommunicating. Read more »
A number of pathological processes affect the limbic system. Patients with longstanding temporal lobe seizures can develop mesial temporal sclerosis, a condition characterized by atrophy of the hippocampus. Neoplasms, both benign and... Read more »
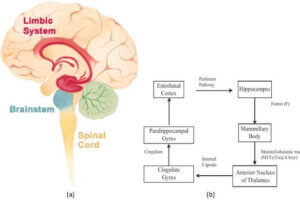
The limbic (derived from the latin limbus, to border or edge) system is a network of structures centered in the medial temporal lobe. These structures or their analogs are found in the... Read more »
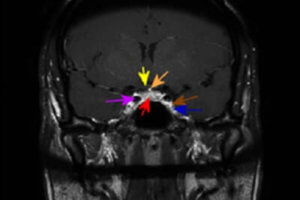
Situated in the midline just above the skull base and bridging the sphenoid and temporal bones, the cavernous sinus is a collection of venous channels that serves as a major conduit for... Read more »
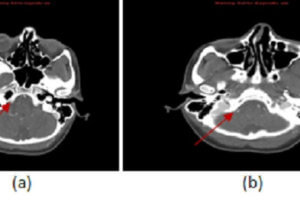
Carotid/vertebral artery dissection is an underdiagnosed disease that can result in substantial morbidity. It has an incidence of 1-1.5/100000 and disproportionately affects young patients. Diagnosis is challenging clinically because the symptoms are... Read more »
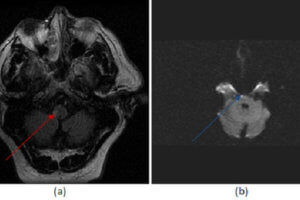
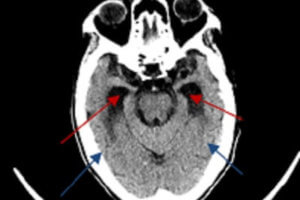
The lateral medullary or Wallenberg syndrome results from an infarct of the lateral medulla from disease in the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) or its branches. The PICA is the first major... Read more »
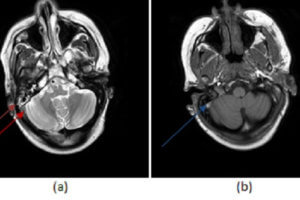
The dural venous sinuses are responsible for draining blood and CSF from the brain. They include the superior and inferior sagittal sinus, straight, transverse, sigmoid and cavernous sinuses. Venous sinus thrombosis can... Read more »
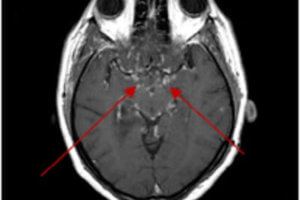
Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory condition with a specific pathology – non caseating (unlike TB) granulomas. The condition affects the lungs , bones and brain. Neurosarcoid occurs in about 5-10% of patients... Read more »
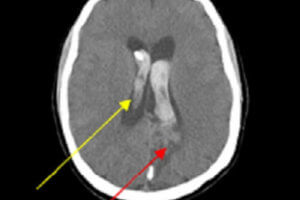
Arteriovenous malformations (AVM’s) are vascular malformations caused by an abnormal communication (arteriovenous shunting) between small arteries and veins without an intervening capillary bed. AVM’s are the most common symptomatic intracranial vascular malformation,... Read more »
