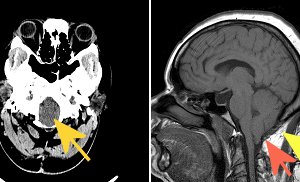
Arnold Chiari 1 malformation is a congenital anomaly of the brain parenchyma characterized by descent of the cerebellar tonsils below the foramen magnum due to a mismatch between the size of the... Read more »
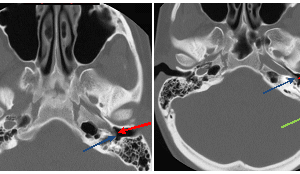
Aberrant course of the internal carotid artery (a-ICA) is a congenital anomaly characterized by the displacement of the ICA posterior and lateral to its expected course. It results from the agenesis of... Read more »
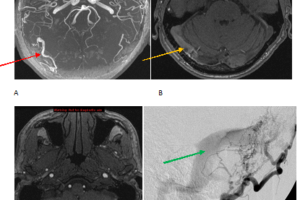
Dural arterio-venous fistulas are a rare but important category of intracranial vascular abnormalities. They are characterized by arterio-venous shunting within the dura and are most commonly a sequelae of trauma. The hypothesized... Read more »
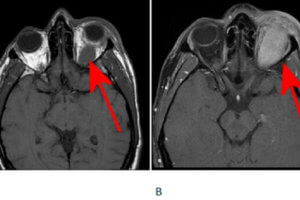
Orbital pseudotumor is the most common cause of a painful orbital mass in adults. It is a mass comprised of inflammatory cells (lymphocytes, macrophages etc) and fibrosis, is typically unilateral and infiltrative. Read more »
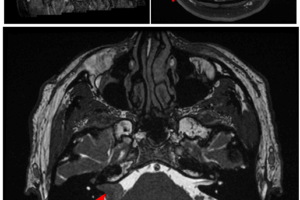
Vestibular schwannomas are benign extra-axial neoplasms that result from proliferation of the schwann cells associated with the eighth (vestibulo-auditory) cranial nerve. The commonly arise in the cerebellopontine angle and may extend along... Read more »
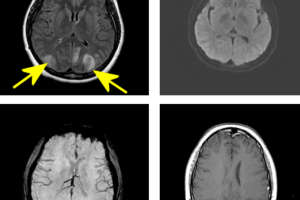
PRES is an disorder of cerebrovascular autoregulation commonly associated with hypertension and previosly referred to as eclampsia. Poor sympathetic regulation of the posterior cerebral arteries makes PRES more likely to involve the... Read more »

Acute infarcts lead to cell swelling in a process called cytotoxic edema. Signal in diffusion weighted MRI (DWI) is inversely related to the degree of brownian motion of intraparenchymal water. When an... Read more »
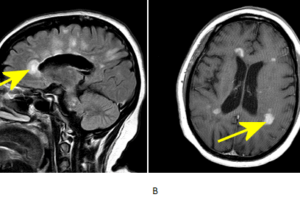
Multiple sclerosis is the most common demyelinaing disease and the most common disabling CNS disease of young adults. The etiology is not certain but likely autoimmune. The disease is characterized by the... Read more »
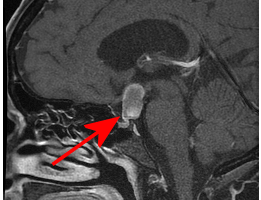
Some differential considerations for a partially cystic sellar/suprasellar mass include a cystic macroadenoma, Rathke’s cleft cyst, cranipopharyngioma, aneurysm, arachnoid cyst and epidermoid. Read more »

There is an extensive differential for multifocal T2/FlAIR hyperintense lesions in the brain parenchyma including neoplasm (metastasis, lymphoma), infection (abscess, septic emboli), infarct (vasculitis), trauma (diffuse axonal injury) and demyelinating disease (multiple... Read more »
