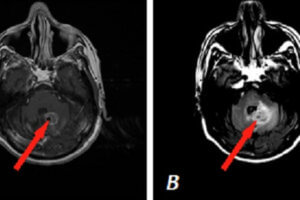
Acute infarcts lead to cell swelling in a process called cytotoxic edema. Signal in diffusion weighted MRI (DWI) is inversely related to the degree of brownian motion of intraparenchymal water. When an... Read more »
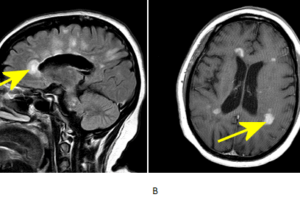
Multiple sclerosis is the most common demyelinaing disease and the most common disabling CNS disease of young adults. The etiology is not certain but likely autoimmune. The disease is characterized by the... Read more »
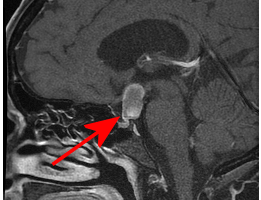
Some differential considerations for a partially cystic sellar/suprasellar mass include a cystic macroadenoma, Rathke’s cleft cyst, cranipopharyngioma, aneurysm, arachnoid cyst and epidermoid. Read more »

There is an extensive differential for multifocal T2/FlAIR hyperintense lesions in the brain parenchyma including neoplasm (metastasis, lymphoma), infection (abscess, septic emboli), infarct (vasculitis), trauma (diffuse axonal injury) and demyelinating disease (multiple... Read more »
Band heterotopia is a congenital disorder that results from the disrupted migration of neurons. Neurons originate in the germinal matrix adjacent to the ventricules and ultimately migrate outward to form the grey... Read more »
Neurosarcoidosis is defined as neuronal, either central or peripheral, involvement of sarcoidosis. About 10% of patients with systematic sarcoidosis have significant neurological deficits as a result of granulomatous lesions, but subclinical disease... Read more »
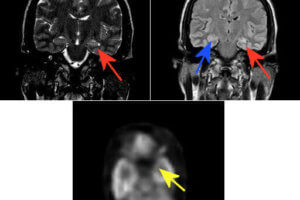
Mesial temporal sclerosis (MTS, also called hippocampal sclerosis) is the most common underlying cause of temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). The etiology is uncertain, although prolonged febrile seizures and limbic encephalitis have been... Read more »
tPA for ischemic stroke was first approved in 1996 based on the result of two NINDS studies that compared outcomes of placebo or IV tPA given in the first 3 hours of... Read more »
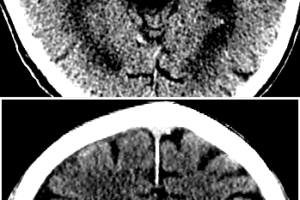
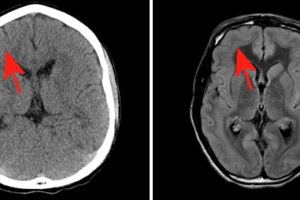
Despite its poor sensitivity for detecting embolic strokes, head CT scan remains the initial imaging modality in the work up of suspected acute stroke. The rationale is to initially rule out hemorrhagic... Read more »