Retinal detachment is a situation where the inner layers of the retina separate from the from the underlying retinal pigment epithelium. This epithelium is called the choroid and is a vascular membrane... Read more »
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is an entity often confused with vestibular neuronitis (VN). It is, however, clinically and pathophysiologically distinct, and it should be relatively easy to distinguish between the two. Read more »
It should first be emphasized that the terms vestibular neuronitis (VN) and acute viral labyrinthitis or epidemic labyrinthitis are not interchangeable. VN is an entity that does not involve the labyrinths at... Read more »

There are three semicircular canals – superior, lateral and posterior. The semicircular canals are integral to maintaining balance and equilibrium with changes in body and head position. Dehiscence of the superior semicircular... Read more »
Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome is a neuro-ophthalmologic diagnosis of exclusion that presents clinically as painful ophthalmoplegia with the ocular motor neuron palsies ipsilateral to the pain. Read more »
Labyrinthitis is an inflammation of the bony labyrinth that impacts on the function of both the vestibular and auditory systems. Inflammation has a variety of potential causes, and therefore there are mulitple... Read more »
Along with vestibular neuronitis (VN) and benign paroxysmal positional neuronitis (BPPV), Meniere’s disease (MD) accounts for a majority of the cases of true vertigo seen by primary care providers. For considerable time,... Read more »
Benign positional vertigo (BPV; AKA benign paroxysmal positional vertigo or BPPV) is a common cause of dizziness characterized by sudden onset of dizziness with position change that resolves in 20-30 seconds. Read more »
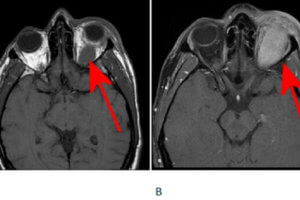
Orbital pseudotumor is the most common cause of a painful orbital mass in adults. It is a mass comprised of inflammatory cells (lymphocytes, macrophages etc) and fibrosis, is typically unilateral and infiltrative. Read more »

 Neurological disorders of the ear and eye.
Neurological disorders of the ear and eye.