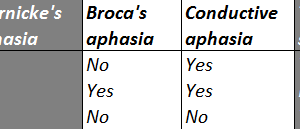
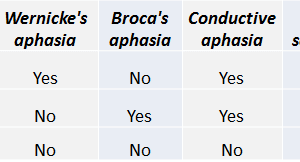
Patients with receptive aphasia can speak clearly (fluently) but cannot understand what others say and have difficulty putting together meaningful sentences. Read more »
Aphasia is defined as a loss of the ability to understand or produce speech, usually caused by damage to the cerebrum. It is important to clinically classify the type of aphasia a... Read more »
Contralateral: adjective; on the opposite side of. Read more »
Ipsilateral: adjective; on the same side of. Read more »
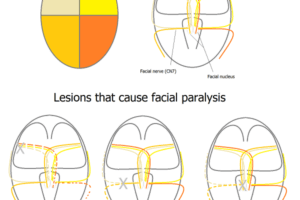
It is important to be able to distinguish central from peripheral causes of facial paralysis. Read more »
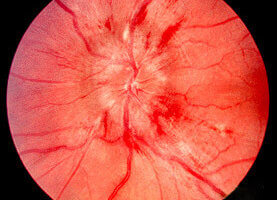
Pseudotumor cerebri, more correctly termed idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), typically presents with headaches, transient visual obscurations, and pulsatile tinnitus. Read more »
Designed to help residents prepare for EEG ABPN milestones, the quiz covers all 5 levels of competency. Residency programs interested in using this for teaching or assessment should contact [email protected]. Read more »
This tool is designed to help residents assess themselves and prepare for the ABPN milestone of Neuroimaging. Residency programs interested in using this for teaching or assessment should contact [email protected]. Read more »
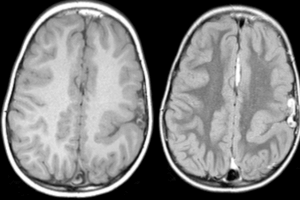
Schizencephaly is a developmental abnormality in brain structure consisting of a cleft from the pia into brain parenchyma, lined by heterotopic gray matter. Read more »
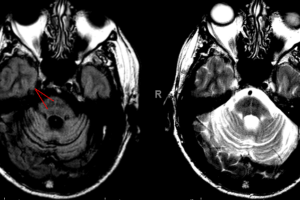
Multi-systems atrophy is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder often initially difficult to differentiate from Parkinson’s Disease. Patients present with autonomic instability (fainting due to orthostasis, fluctuating heart rate, urinary incontinence or difficulty emptying... Read more »
