Neurofibromatosis is a condition that can involve almost any organ system. It can be divided into two major subtypes, neurofibromatosis 1 (NF-1, traditionally known as Von Recklinghausen Disease) and neurofibromatosis 2 (NF-2). A third variant is known as segmental NF, disease limited to a single body region; this condition is an autosomal dominant condition. This article focuses on NF-1.
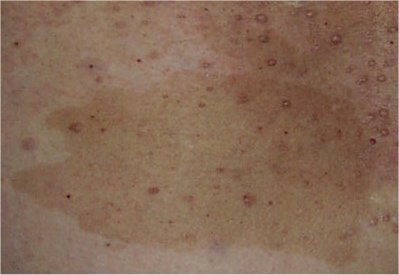
Café au lait spots
Café au lait macules develop during the first 3 years of life although most patients are not born with them. They are often the clinical finding that prompts parents to seek medical attention for their child. The neurofibromas form in late adolescence. Patients may also complain of pain caused by neurofibromas, i.e. pathologic fractures, or hypertensive headaches due to pheochromocytoma.

Figure: Café au lait spot
Café au lait spots typically have an irregular shape and an evenly pigmented, brown color. Affected children will have 6 or more such spots that are 1.5 cm or greater in diameter. Although 1 or 2 café au lait macules are commonly encountered in healthy individuals, less than 1% of healthy children have 3 or more. Axillary freckling, known as the Crowe sign, is a helpful diagnostic feature in neurofibromatosis. Both axillary freckling and inguinal freckling often develop during puberty.
There are many types of bone involvement, including pseudoarthrosis of the tibia, bowing of the long bones, orbital defects, mild scoliosis, and localized bony hypertrophy, especially on the face. Neurofibromas are the most common benign tumor of NF-1 and can be found at any point along a nerve. They are divided into three subtypes, cutaneous, subcutaneous, and plexiform.
Neurologic abnormalities of neurofibromatosis
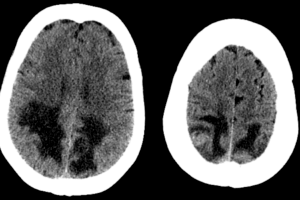
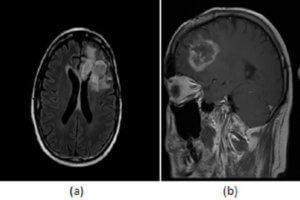
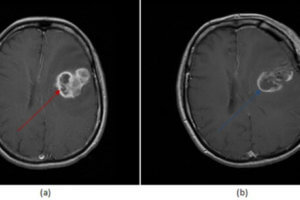
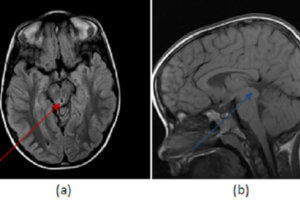
There are also a wide variety of neurologic abnormalities, including acoustic nerve involvement, gliomas of the optic nerve, astrocytoma, meningioma, intramedullary glioma, and ependymoma. These tumors may cause multiple neurologic symptoms including increased intracranial pressure, seizures, ataxia, or cranial nerve abnormalities. An example of neurofibromas can be seen on the neurofibromatosis page.
Schwannomas are uncommon in patients with NF-1, but in NF-2, they are the most common tumor. They typically involve cranial and peripheral nerves. The presence of a unilateral vestibular schwannoma is indication to include NF-2 in a differential diagnosis.
Learning disabilities are common in patients with NF-1. These may include neuromotor dysfunction and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. In addition, these patients have an increased incidence of endocrinologic problems including short stature and growth hormone deficiency, sexual precocity, and pheochromocytoma.
Patients with NF-1 have an average life expectancy that is at least 10 to 15 years less than average. The most common cause of death is malignancy. Hypertension is also associated with significant mortality. Primary prevention of NF-1 complications is not currently possible. Laboratory testing for NF-1 mutations is difficult, and at this time, the benefits of population-based screening do not outweigh the costs of screening.
Von Recklinghausen’s Disease mnemonic
17-letters has Von Recklinghausen on human chromosome 17.