Also known as Von Recklinghausen’s disease, neurofibromatosis (NF) is an inherited neurocutaneous syndrome with systemic manifestations, the most notable of which is the occurrence of multiple neurofibromas.
Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis

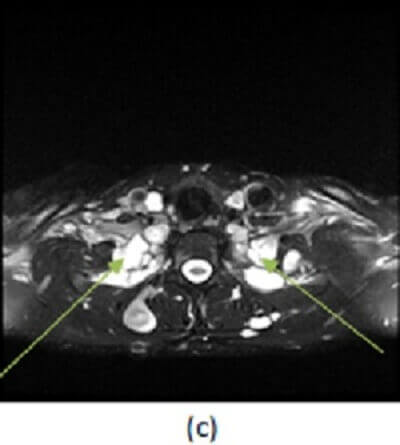
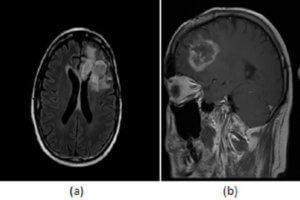
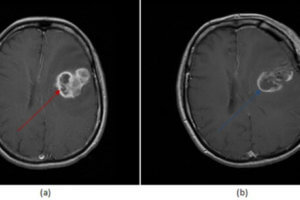
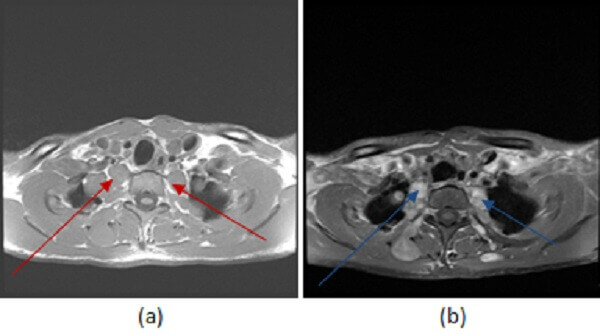
Figure 1: (a, red arrow) axial T1, (b, blue arrow) T1 post contrast and (c, green arrow) T2 with fat suppression demonstrate multiple T2 hyperintense, homogenously enhancing ovoid and dumbbell shaped masses, many in contiguity with the neural-foramina, most consistent with neurofibromatosis.
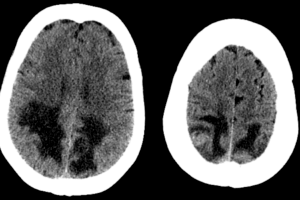
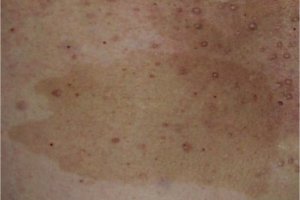
Two types of NF are recognized and they have different manifestations in the central and peripheral nervous system. Type 1 NF is characterized clinically by the presence of café au lait spots. Neural manifestations include the presence of plexiform (multiple, confluent) neurofibromas, macrocephaly, dysplasia of the sphenoid wing, optic nerve gliomas, poorly defined lesions of the white matter that lack mass effect, and vascular anomalies, specifically intimal hyperplasia leading to intracranial stenosis and aneurysms.
Neurofibromatosis type 2, on the other hand is characterized by the presence of multiple meningiomas, schwannomas, and ependymoma’s. NF 2 also has a pathognomonic finding – bilateral vestibular schwannomas .Cranial nerves 3,5 and 12 are other less common sites for schwannomas in NF 2. NF 2 is less common, with an incidence of about 1:25,000.It usually presents with hearing loss and vertigo in patient’s aged 20-40.