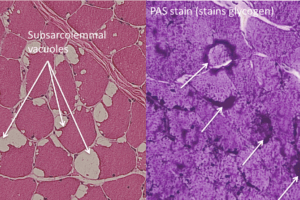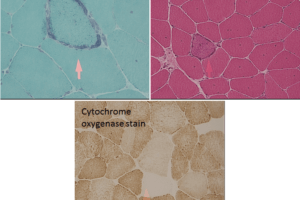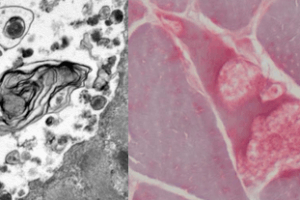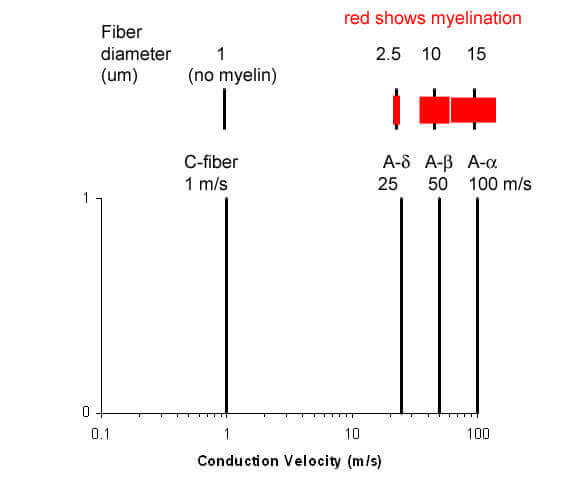
Fibers within a peripheral nerve are classified by conduction speed and diameter.
 Fast fibers (A-alpha and A-beta fibers) are fibers of the DC-ML system, so carry light touch, proprioception and vibratory information. Specifically, A-alpha fibers carry proprioception while A-beta fibers carry fine touch.
Fast fibers (A-alpha and A-beta fibers) are fibers of the DC-ML system, so carry light touch, proprioception and vibratory information. Specifically, A-alpha fibers carry proprioception while A-beta fibers carry fine touch.
Slow fibers (A-delta and C fibers) are fibers of the anterolateral system, so carry pain and temperature information. A-delta fibers are lightly myelinated, so conducted slowly. C-fibers are unmyelinated, so their conduction velocity is the slowest. In fact, you often perceive a painful stimulus in two stages: the first, rapid sensation is carried by A-delta fibers and can mediate a withdrawal reflex (imagine touching a hot pan and pulling away immediately), the second slower sensation is carried by C-fibers and produces the long-lasting painful sensation (the burning “ow” sensation that comes half a second after touching the hot pan).