Loss of motor neurons in either the motor cortex or the anterior horn of the spinal cord causes paralysis. A variety of diseases affect these neurons, and specific diseases affect either the upper motor neuron or the lower motor neuron differentially.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Lou Gehrig’s disease) is the best know of the motor neuron disease, and is characterized by both upper motor neuron and lower motor neuron signs. While ALS affects motor neurons in the ventral horn, accounting for the lower motor neuron findings, it also affects neurons in the primary motor cortex, accounting for the upper motor neuron signs.

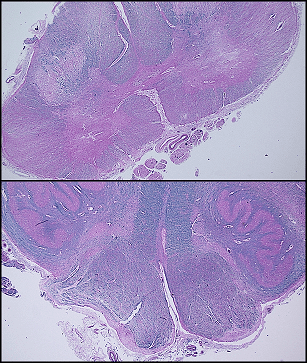
Caption: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (autopsy) Top. Combined H&E and LFB staining: Spinal cord with pink (loss of blue LFB staining) lateral columns secondary to axonal in descending cortical spinal tracts. Bottom. Combined H&E and LFB staining. Pyramids demonstrate slightly more pink staining corresponding to mild axonal loss in the region.
Primary lateral sclerosis affects upper motor neurons, resulting in spasticity. It can have a slower progression than ALS, with average disease progression of ~20 years. here is both a familial and sporadic form of PLS. Motor evoked potentials are absent, but peripheral motor nerves are intact. PLS lacks significant lower-motor neuron findings (although mild denervation is sometimes found). The prevalence of PLS is unclear, but is significantly less than that of ALS.
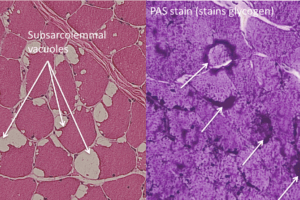
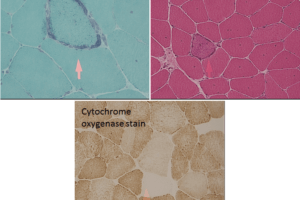
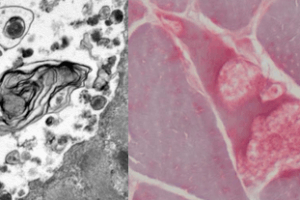
The spinal muscular atrophies are prototypical lower-motor neuron diseases. They constitute a group of genetic disorders with an overall incidence of ~1 in 10,000. Types 1-3 manifest during infancy, while type 4 has an adult onset. Presenting symptoms include widespread weakness and muscle atrophy, including somatic and bulbar muscle groups. EMG needle studies show neurogenic recruitment patterns.
Infectious motor neuron diseases: Historically, infection with the poilo virus was the most common cause of motor neuron disease, with poliomyelitis affecting 350,000 people as recently ast 1988. Today, infection with the West Nile Virus is more likely than poiio to damage motor neurons and cause paralysis.
References
Armon, Carmel. Primary Lateral Sclerosis http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1171782-overview#showall
Tsao, Bryan, Spinal Muscular Atrophy http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1181436-overview