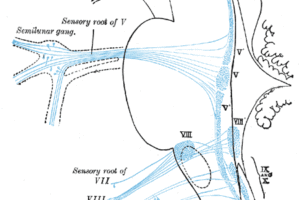
Trigeminal neuralgia (TGN) is a neuritis of the fifth cranial nerve, the trigeminal nerve. It is estimated to occur at a rate of 1.6 per thousand (internationally.) It occurs at a frequency roughly the same in men and women.
Etiology of Tic Douloureaux
Its etiology continues to be much debated. One theory proposes that peripheral injury increases afferent firing in the nerve. Another theory implicates a failure of central inhibitory mechanisms. Anatomically, an abnormal vascular course of the superior cerebellar artery, an aneurysm, a brain tumor, and chronic meningeal inflammation may all irritate trigeminal nerve roots.
Clinical Presentation of Tic Douloureaux
Patients present with pain that is brief and paroxysmal, characterized as stabbing or shock-like. It is usually severe. Its distribution, since this is a peripheral problem, is along one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve and is usually unilateral. It lasts for a few seconds, but continues throughout the day. The associated facial numbness will come on early in the disease and is often not recalled by patients when compared to the pain.
Physical examination is often normal. It may also be difficult to perform since some patients have trigger points, and the fear of an examination activating one of these trigger points leads to significant patient apprehension and guarding. However, doing a thorough exam is important because any abnormality implicates some pathology other than tic.
Idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia is more common in the sixth decade. Secondary tic is more common in the second and third decades. Multiple sclerosis and neurofibromatosis are two of the diseases that can cause a secondary tic.
Treatment of Tic Douloureaux
The initial treatment for tic should be neuroleptic medications. Tegretol and Lioresal, often in combination, are the standard accepted drugs of choice. Visualizing the trigeminal nerve root with a brain MRI (cranial nerve protocol) can be helpful in not only ruling out unusual pathology, but also determining whether of not surgical intervention will be successful if medical therapy fails.
Guidelines for the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia call for steriotactic radiosurgery in patients with intractable pain.