Cefepime is a cephalosporin antibiotic typically used when broad spectrum coverage including Pseudomonas aerigonsa is needed. However, it can produce cefepime neurotoxicity with encephalopathy, myoclonus, reversible aphasia, and/or convulsive or subclinical seizures. Read more »
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) is one of the most common generalized epilepsy syndromes and typically presents in the teen years. Like absence epilepsy, it is considered a primary generalized epilepsy, rather than... Read more »
Absence epilepsy is a type of primary generalized epilepsy in children, and usually presents as staring spells. Read more »
We are honored to present an interview with the world-renowned epileptologist Dr. John Ebersole on the occasion of his retirement from the University of Chicago. Read more »
There are many variants on EEG that are considered normal and yet might be confused with epileptiform activity. These benign EEG variants are often found in only certain subpopulations: either young or... Read more »
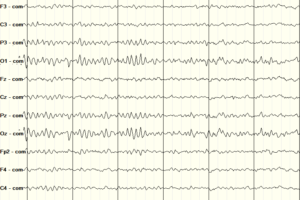
Sleep stages can be identified by the appearance of characteristic electrical patterns on EEG. Sleep can initially be broken down into REM-sleep and non-REM sleep, with further parcelization of non-REM sleep into... Read more »
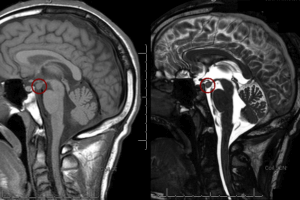
The MR images show an abnormal growth hanging down from the hypothalamus. This is a hypothalamic hemartoma, which in some cases can be a type of grey matter heterotopia within the tuber cinereum.... Read more »
Landua Kleffner Syndrome is one of a spectrum of childhood epileptic disorders and presents with acquired aphasia (loss of the ability to speak or understand speech after initially being able to). Read more »
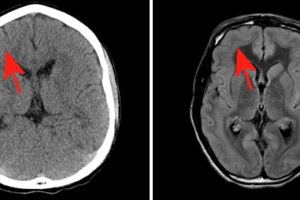
Band heterotopia is a congenital disorder that results from the disrupted migration of neurons. Neurons originate in the germinal matrix adjacent to the ventricules and ultimately migrate outward to form the grey... Read more »
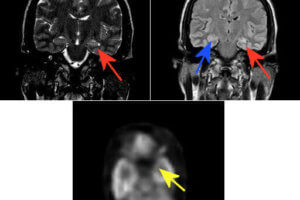
Mesial temporal sclerosis (MTS, also called hippocampal sclerosis) is the most common underlying cause of temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). The etiology is uncertain, although prolonged febrile seizures and limbic encephalitis have been... Read more »

 Pediatric and adult epilepsy disorders.
Pediatric and adult epilepsy disorders.