Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II (CPT) deficiency is the most common inherited lipid-metabolism disorder in skeletal muscle. Read more »
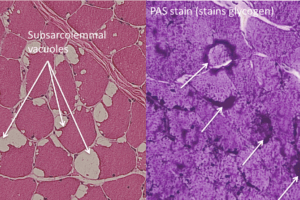
McArdle disease is a glycogen storage disease in which the enzyme muscle myophosphorylase is deficient. It is commonly known as glycogen storage disease V. Read more »
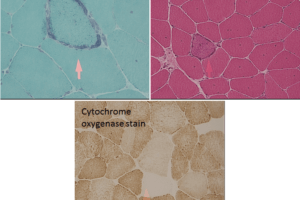
Mitochondrial myopathy can be caused by metabolic abnormalities related to mutations in the mitochondrial genome or mutations in the somatic genome that produce abnormal mitochondrial proteins. Read more »
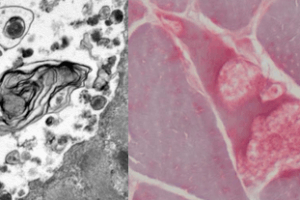
Pompe disease is an autosomal recessive lysosomal glycogen storage disease. Mutations in the acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) gene on chromosome 17q25.2-q25.3 result in abnormal accumulation of glycogen within lysosomes and subsequent lysosomal dysfunction. Read more »
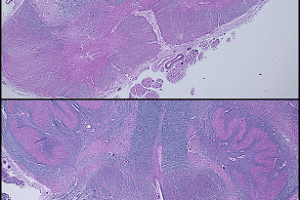
Loss of motor neurons in either the motor cortex or the anterior horn of the spinal cord causes paralysis. A variety of diseases affect these neurons, and specific diseases affect either the... Read more »
Brief review of the clinical pharmacology of acetylcholine, acetylcholinesterase and the ach receptor. Read more »
A summary of high yield clinical topics related to acetylcholine chemistry and acetylcholine receptors. Read more »
Acetylcholine is one of the major neurotransmitters in the mammalian nervous system, found at all neuromuscular junctions, at all synapses in autonomic ganglia, at a variety of locations in the CNS and... Read more »
The Nernst equation describes the voltage across a cell membrane at which there would be no net flow of a particular ion (assuming there are ion channels that passed that ion). This... Read more »
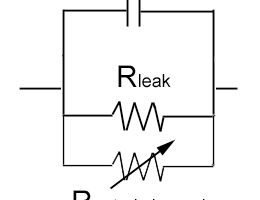
The electrical properties of neurons can described in terms of electrical circuits. This approach helps us understand how a neuron behaves when current flows into it (for example, when ion channels open),... Read more »

 Neurologic disorders of the peripheral nervous system and muscles, with EMG/NCV studies.
Neurologic disorders of the peripheral nervous system and muscles, with EMG/NCV studies.